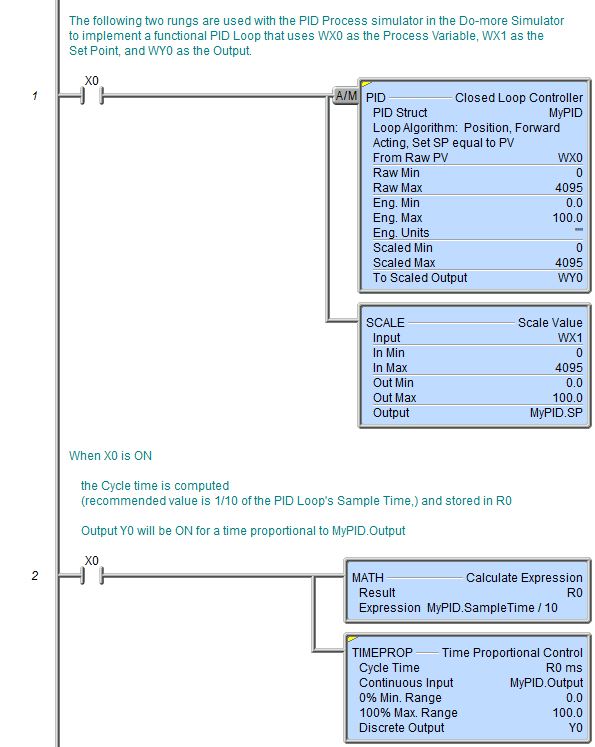
Topic: DMD0144
TIMEPROP - Time Proportional Control
The Time Proportional Control (TIMEPROP) instruction is used to convert the continuous control output variable interpreted as a percentage to time proportioning control suitable for a discrete output. Time-proportional control is a form of pulse-width modulation, which is a mathematical technique that allows a feedback controller to use an on/off or discrete actuator as if it were a continuous actuator capable of generating control outputs anywhere between 0% and 100%. This control method is used to turn the actuator on and off for periods of time that are proportional to the desired control output.
The Closed Loop Controller (PID) instruction generates a smooth control output signal across a numerical range, typically 0% to 100%. This is called continuous control because the output is at some level continuously. PID control is applied in an ON/OFF control system by adding a time base within the controller. For each preset time interval, the Cycle Time, the controller will proportion the ON and OFF time depending on the magnitude of the output and the PID tuning values selected.
ON Time = ----------------------------------------
OFF Time = Cycle Time - ON Time
A good example of time proportional control is a hot-air balloon following a path (the Set Point) across some mountains. The balloon pilot turns the burner on and off alternately, which is his control output. The large mass of air in the balloon effectively averages the effect of the burner, converting the bursts of heat into a continuous effect: slowly changing balloon temperature and ultimately the altitude, which is the process variable.
Parameters:
Note: Use the F9 key (Element Browser) or Down-Arrow key (Auto-Complete) at any time to see a complete list of the memory locations that are valid in the current field of the instruction.
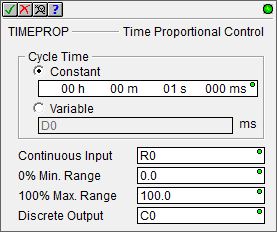
Cycle Time - designates the
amount of time that will be divided into an ON and an OFF portions. It
is recommended that this value be set to 1/10 of the Sample Time of the
PID Loop that is generating the continuous output value.
Constant - specified using the Time format (HH : MM : SS : mmm).
The maximum Cycle Time value in this form
is 569 hours, 31 minutes, 23 seconds, and 647 milliseconds. If needed,
the value entered for the Cycle Time will be normalized to its standard
value. For example, if you entered a value of
When editing the Constant Preset value, the following keystrokes are available
to make entering the value easier and faster:
h - takes you to the Hours field
m - takes you to the Minutes field
s - takes you to the Seconds field
mm - takes you to the Milliseconds field
Variable - designates a location that contains the total number of milliseconds desired for the Cycle Time. This can be any readable numeric location.
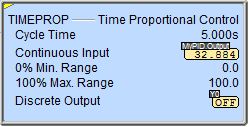
Continuous Input - designates the location to use as the Input value. This can be any readable numeric location, but it is typically the output of a Closed Loop Controller (PID) instruction ( <PID Reference>.Output ).
The time proportioning control must match the resolution of the Continuous Input (typically 0% to 100%). For example, when using PID .Output values the range would be 0.0 to 100.0, and for 12-bit analog inputs the range would be 0 to 4095. The following two fields allow for adjusting the scale factor:
0% Min Range - designates the minimum value of the Continuous Input Range. This can be any constant value or any readable numeric location.
100% Max Range - designates the maximum value of the Continuous Input Range. This can be any constant value or any readable numeric location.
Discrete Output - designates the BIT location in the PLC that will be turned ON and OFF. This can be any writable bit location.
Status Display:
The yellow triangle in the upper left corner indicates this is a Multi-Scan instruction.
See Also:
TIMEPROP - Time Proportional Control
Rung Example: