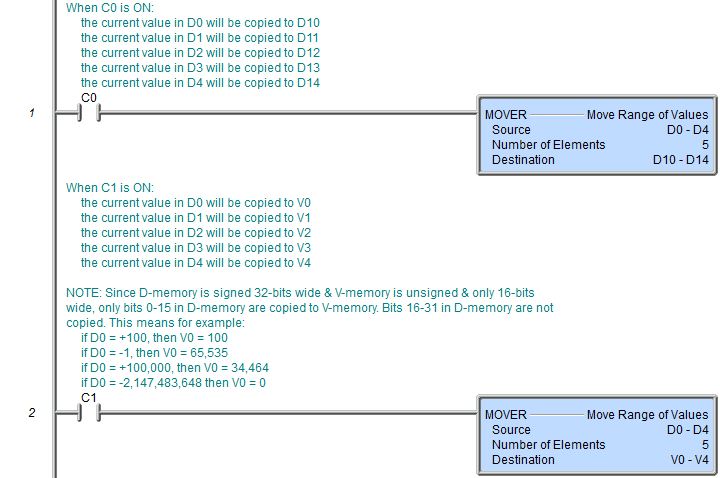
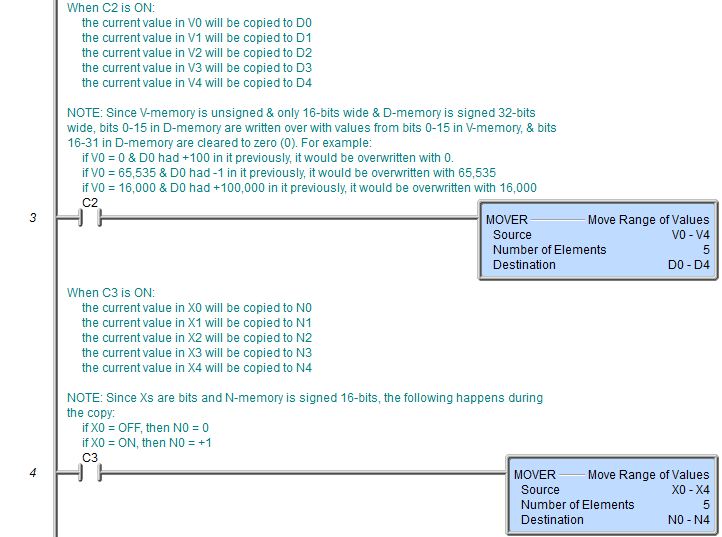
Topic: DMD0009
MOVER - Move Range of Values
The Move Range of Values (MOVER) instruction is used to move the values from one range of memory locations to a second range of memory locations in the Do-more controller.
If the Source range and Destination range are different block types, any data conversion that is required will automatically be performed during the copy operation. For example, if the source range is D0 to D9 and the Destination range is R0 to R9, each value will be converted to a floating point number as it is copied.
If the size of the elements in the Destination range are smaller than the elements in the Source range, the values will be truncated during the copy operation. For example, if the source range is D0 to D7 and the Destination Range is V0 to V7, the low Word of each Dx (32-bit) location will be moved to the corresponding Vx (16-bit) location.
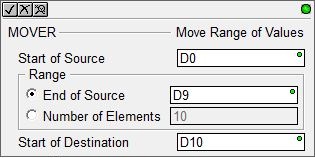
The Move Range of Values instruction cannot move entire structures - the Copy Memory Range (MEMCOPY) instruction is the proper instruction to copy entire structures.
Parameters:
Note: Use the F9 key (Element Browser) or Down-Arrow key (Auto-Complete) at any time to see a complete list of the memory locations that are valid in the current field of the instruction.
Start of Source - designates the first memory location of the data to copy. This can be any readable, non-structure numeric location.
Range - specifies the extent
of the range of values to copy, this can be specified in one of the following
two ways:
End of Source - designates the last memory location in the source range of values to copy. This memory location must be in the same block as the Start of Source, and the ID of the end memory location must be greater than the ID of the source memory location.
Number of Elements - specifies the number of elements in the range. This can be any constant value up to the number of memory locations in the block, or any readable numeric location.
Start of Destination - designates the first memory location of the where the data is to be copied. This can be any readable, non-structure numeric location.
See Also:
MOVER - Move Range of Values
Rung Examples: