Topic: DM0005
MAPIO - Map Inputs and Outputs
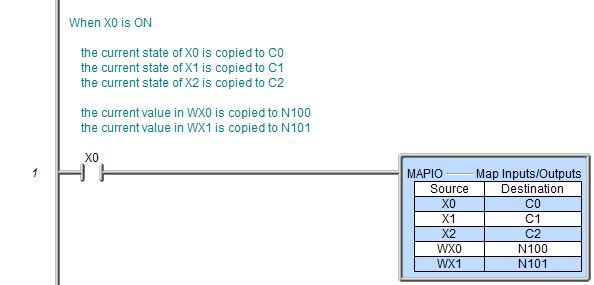
 The Map Inputs/Outputs (MAPIO) instruction maps real-world I/O
to specific elements in situations where the I/O may move but they are
mapped to fixed element addresses. When the instruction is enabled the
values of the Source variables are copied to the Destination variables.
The Map Inputs/Outputs (MAPIO) instruction maps real-world I/O
to specific elements in situations where the I/O may move but they are
mapped to fixed element addresses. When the instruction is enabled the
values of the Source variables are copied to the Destination variables.
When used as intended it will map Discrete Inputs (X) to internal Bits (C) and Analog Inputs (WX) to Numeric elements (N), and then internal Bits (C) to Discrete Outputs (Y) and internal Numeric elements (N) to Analog Outputs (WY).
There will typically be a pair of Map Inputs/Outputs Instructions: one at the top of scan for mapping the Discrete and Analog inputs to internal memory, and one at the bottom of the scan for mapping internal memory to Discrete and Analog outputs.
This instruction can be used to move any element to any element, but its primary purpose is as an instruction for mapping real-world I/O to internal memory. The System Tasks $tTopOfScan and $tBottomOfScan are the recommended code blocks to place this pair of instructions.
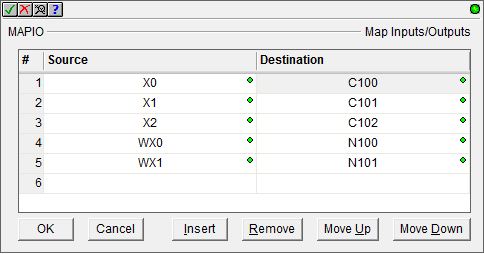
Row Editor Keys:
The following functions are used to add or remove rows, edit existing rows or reorganize the rows in the instruction.
Ok - closes the editor, saving any changes that have been made.
Cancel - closes the editor, discarding any changes that have been made.
Insert - inserts a new row in the instruction before the currently selected row.
Remove - removes the currently selected row.
Move Up - moves the currently selected row up one row.
Move Down - moves the currently selected row down one row.
Parameters:
Note: Use the F9 key (Element Browser) at any time to see a complete list of the memory locations that are valid in the current field of the instruction.
Source - specifies the input
locations
when mapping inputs this specifies the real-world analog or discrete input point to map
when mapping outputs this specifies the internal element that is mapped to the real-world discrete or analog output point
Destination - specifies the
output locations
when mapping inputs this specifies the internal element to map to the discrete or analog point
when mapping outputs this specifies the real-world discrete or analog output I/O point to map
See Also:
MAPIO - Map Inputs and Outputs
Rung Example: